"In chemistry, a disulfide bond (Br.E. disulphide bond) is a covalent bond, usually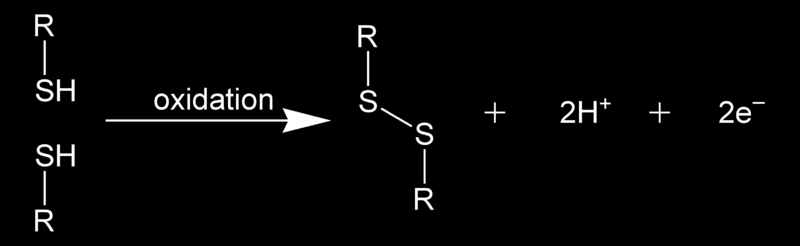 derived by the coupling of two thiol groups. The linkage is also called an SS-bond or disulfide bridge. The overall connectivity is therefore R-S-S-R. The terminology is widely used in biochemistry. In formal terms, the connection is a persulfide, in analogy to its congener, peroxide (R-O-O-R), but this terminology is obscure and is no longer used (except in reference to R-S-S-H or H-S-S-H compounds)."
derived by the coupling of two thiol groups. The linkage is also called an SS-bond or disulfide bridge. The overall connectivity is therefore R-S-S-R. The terminology is widely used in biochemistry. In formal terms, the connection is a persulfide, in analogy to its congener, peroxide (R-O-O-R), but this terminology is obscure and is no longer used (except in reference to R-S-S-H or H-S-S-H compounds)."
"The disulfide bond is strong, with a typical bond dissociation energy of 60 kcal/mole (251 kJ mol-1). However, being about 40% weaker than C-C and C-H bonds, the disulfide bond is often the "weak link" in many molecules. Furthermore, reflecting the polarizability of divalent sulfur, the S-S bond is susceptible to scission by polar reagents, both electrophiles and especially nucleophiles:"
- RS-SR + Nu- → RS-Nu + RS-
"The disulfide bond is about 2.05 Å in length, about 0.5 Å longer than a C-C bond. Rotation about the S-S axis is subject to a low barrier. Disulfides show a distinct preference for dihedral angles approaching 90°. When the angle approaches 0° or 180°, then the disulfide is a significantly better oxidant."