 Tuesday, March 12, 2013 at 10:47AM
Tuesday, March 12, 2013 at 10:47AM "Polyanhydrides are a class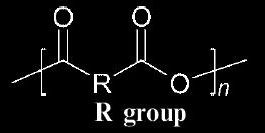 of biodegradable polymers characterized by anhydride bonds that connect repeat units of the polymer backbone chain. Their main application is in the medical device and pharmaceutical industry. In vivo, polyanhydrides degrade into non-toxic diacid monomers that can be metabolized and eliminated from the body. Owing to their safe degradation products, polyanhydrides are considered to be biocompatible."
of biodegradable polymers characterized by anhydride bonds that connect repeat units of the polymer backbone chain. Their main application is in the medical device and pharmaceutical industry. In vivo, polyanhydrides degrade into non-toxic diacid monomers that can be metabolized and eliminated from the body. Owing to their safe degradation products, polyanhydrides are considered to be biocompatible."
"The characteristic anhydride bonds in polyanhydrides are water-labile (the polymer chain breaks apart at the anhydride bond). This results in two carboxylic acid groups which are easily metabolized and biocompatible. Biodegradable polymers, such as polyanhydrides, are capable of releasing physically entrapped or encapsulated drugs by well-defined kinetics and are a growing area of medical research. Polyanhydrides have been investigated as an important material for the short-term release of drugs or bioactive agents. The rapid degradation and limited mechanical properties of polyanhydrides render them ideal as controlled drug delivery devices."
Reader Comments